Your loan-to-value ratio guide
When taking out a loan for a new home or car, it’s important to understand the loan-to-value (LTV) ratio. The item’s value, your down payment (or lack thereof) and the amount you’re intending to borrow can all affect your loan’s terms.
Our handy infographic will help you. We’ve broken down what an LTV ratio is, why it’s important and how it affects your mortgage, auto loan or home equity loan so you can borrow with confidence.
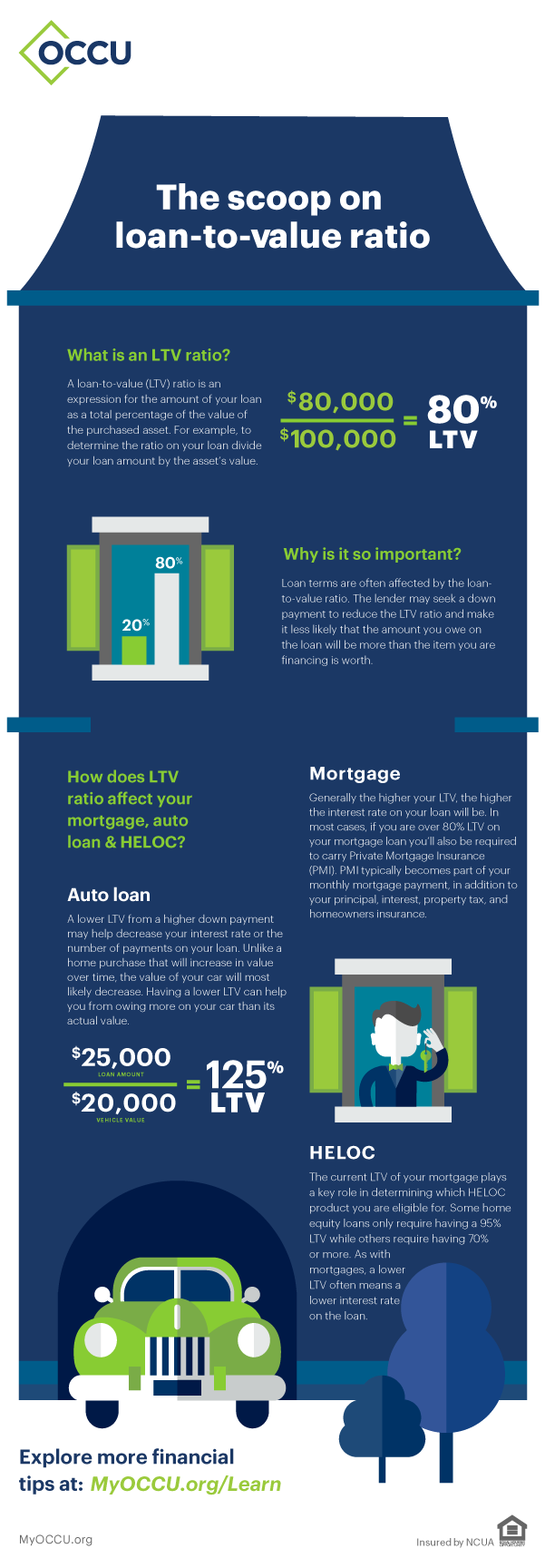
The Scoop on Loan-To-Value Ratio
What is a Loan-To-Value Ratio?
A Loan-To-Value (LTV) is an expression for the amount of your loan as a total percentage of the value of the purchase asset. For example, to determine the ratio on your loan divide your loan amount by the asset’s value.
EXAMPLE: $80,000 (Loan amount)
_________________________ = 80% (LTV)
$100,000 (Asset value)
Why is it important?
Loan terms are often affected by the loan-to-value ratio. The lender may seek a down payment to reduce the LTV ratio and make it less likely that the amount you owe on the loan will be more than the item you are financing is worth.
How does LTV Ratio affect your Mortgage, Auto Loan & Home Equity Line of Credit?
Mortgage
Generally, the higher your LTV, the higher the interest rate on you loan will be. In most cases, if you are over 80% LTV on your mortgage loan you’ll also be required to carry Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI). PMI typically becomes part of your monthly mortgage payment, in addition to your principal, interest, property tax, and homeowner's insurance.
Auto loan
A lower LTV from a higher down payment may help decrease your interest rate or the number of payments on your loan. Unlike a home purchase that will increase in value over time, the value of your car will most likely decrease. Having a lower LTV can help you from owing more on your car than its actual value.
$25,000 (Loan amount)
_________________________ = 125% (LTV)
$20,000 (Vehicle value)
Home equity line of credit.
The current LTV of your mortgage plays a key role in determining which home equity product you are eligible for. Some home equity loans only require having a 95% LTV while others require having a 70% or more. As with mortgages, a lower LTV often means a lower interest rate on the loan.